A report by the respected economists, Oxera, reveals how the mass market rollout of Gigabit broadband will help fight climate change by revolutionizing healthcare, transforming workplaces and enriching social and digital interactions.
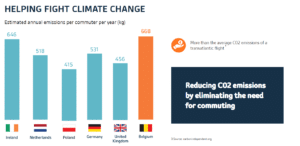
New technologies have the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions. Currently, many activities that a person undertakes in their day-to-day lives require travelling from one place to another. Reductions in carbon emission can be achieved by decreasing that need for regular travel. Some of the activities that are enabled by gigabit connections, such as visiting a doctor and working from home can reduce the need to travel and thus reduce carbon emissions.
In the three areas set out below, healthcare, workplaces and digital and social interaction, new and improved technologies enabled by gigabit connections may reduce the need to travel.
Revolutionized healthcare
Gigabit connectivity may alleviate the requirement for both patient and doctors to be physically present in the same location. The availability of home-based scanning devices and high quality video-streams could enable remote monitoring and remote diagnosis. Improved video streams and scanning devices could enable both patients and medical specialists to attend or carry out consultations from home. This would reduce the carbon emissions from the medical professional, the patient or both travelling to the hospital.
Transformed workplaces
Gigabit connections and technology will support more immersive and responsive collaboration via remote workplaces, reducing the need to commute. Through holographic conferencing, augmented reality presence and virtual conference rooms professionals will be able to work seamlessly without having to physically be in the same room as other colleagues. The COVID-19 crisis has shown that, thanks to widespread availability of ultrafast and reliable broadband, many industries can work from home without disruption, which has already had an impact on commuter emissions.
Social and digital interactions
Climate benefits may also be achieved through improved digital and social interaction. Through a transformative application referred to as virtual reality learning, students could be able to learn through virtual experiences at remote locations without the need to travel. Future use of volumetric videos for immersive entertainment could allow users to virtually attend a football match rather than needing to be present at the stadium.
Gigabit connectivity plays a vital role in unlocking new technology and applications which can reduce carbon emissions. Due to the global pandemic, we have started to see the acceleration of these technologies being rolled out on mass and adopted by workplaces, hospitals and individuals which is leading to a decrease in the need for reoccurring travel.
For full information on Oxera’s findings, visit section 5.4 of the report.